Internal structure and function of the battery
The original function of the battery in the engine compartment is well known. Without the battery the vehicle cannot be started. In addition to the starter motor, the spark plugs, glow plugs, lights and electronic applications all require electrical energy. What is the structure of a battery? How does it work?
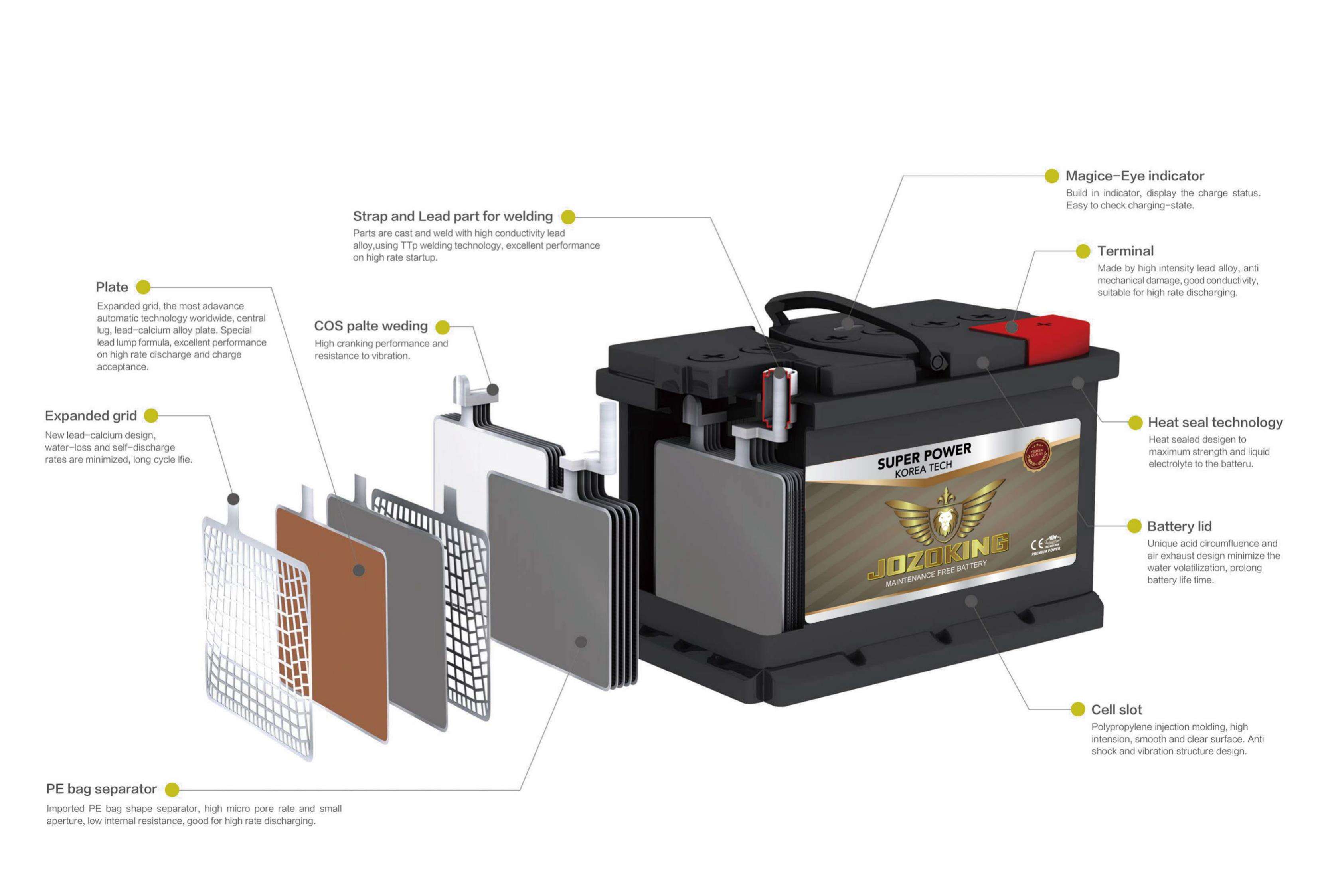
The internal structure of the battery
Positive electrode:
·Positive plate: In a lead-acid battery, the positively charged plate (active material) consists of lead oxide (PbO2) which is immersed in an electrolyte.
Positive grid: The positive grid consists of a lead alloy and is used to hold the active material and as a current collector.
Negative electrode:
The negatively charged plate (active material) consists of pure lead (Pb), which is also immersed in an electrolyte.Like the positive plate, this also consists of a lead alloy and serves the same purpose.
The electrodes with different charges are separated by a separator.
The electrolyte is a mixture of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and distilled water. This electrolyte can be in liquid form (as in conventional wet batteries or in the enhanced EFB technology), in gel form, or bound in a glass mat (as in AGM technology for newer start-stop applications).
Multiple positive electrodes form a positive electrode plate group, and multiple negative electrodes form a negative electrode plate group. The negative plate group and the positive plate group form a group together to form a unit.
A conventional starter battery consists of 6 cells connected in series, each with a nominal voltage of 2 V, which results in a voltage of exactly 12.72 V when the battery is fully charged. The capacity and cold start capability of the battery are determined by the number of plates per battery.
The more plates a battery contains and therefore creates a larger surface, the more cold cranking power (CCA) the battery can provide. However, if fewer but thicker plates are used in the battery, the cycle stability will increase.
The function of the battery
A car battery stores energy in chemical form and converts it into electrical energy. In this elector-chemical process, four materials react with each other, so that chemical energy becomes electrical energy.
· Hydrogen (H)
· Oxygen (O2)
· Lead (Pb)
· Sulfur (S)